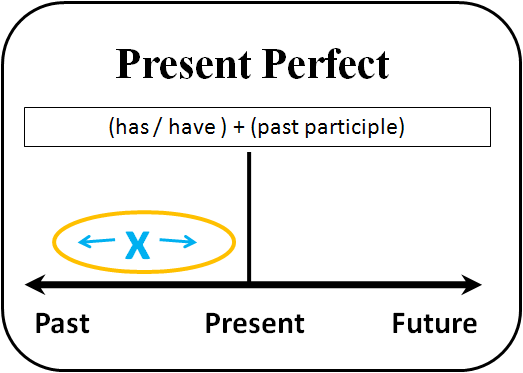
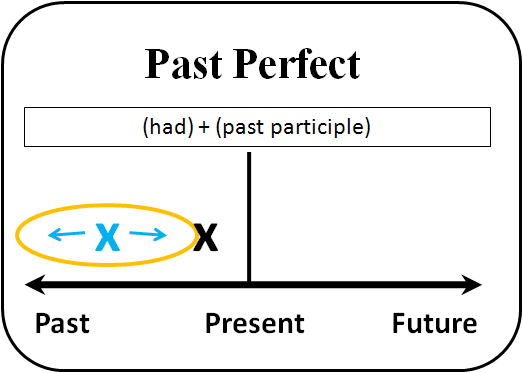
Pelajari situasi berikut:
Sarah went to a party last week. Paul went to the party too but they didn’t see each other. Paul went home at 10.30 and Sarah arrived at 11 o’clock. So, When Sarah arrived at the party, Paul wasn’t there. He had gone home.
Had gone us the past perfect (simple):
I/we/they/you/he/she/it + had + past participle (Verb 3)
Terkadang kita menggunakan tense ini untuk menjelaskan sesuatu yang terjadi di masa lampau:
- Sarah arrived at the party.
Ini adalah titik awal dari kegiatan yang dibicarakan. Maka, jika kita ingin membicarakan sesuatu yang terjadi di masa lampau, kita bisa menggunakan past perfect tense:
- When Sarah arrived at the party, Paul had already gone home.
Contoh lain:
- When we got home last night, we found that somebody had broken into the flat.
- Karen didn’t want to come to the cinema with us because she had already seen the film.
- At first I thought I’d done the right thing, but I soon realised that I’d made a serious mistake.
- The man sitting next to me on the plane was very nervous. He hadn’t flown before. / He had never flown before.
Had done (past perfect) adalah masa lampau dari have done (present perfect). Bandingkan:
Present perfect:
- Who is that woman? Ive never seen her before.
- We aren’t hungry. We’ve just had lunch.
- The house is dirty. They haven’t cleaned it for weeks.
Past perfect:
- I didn’t know who she was. I’d never seen her before. (=sebelum waktu dibicarakan)
- We weren’t hungry. We’d just had lunch.
- The house was dirty. They hadn’t cleaned it for weeks.
Bandingkan amtara past perfect (I had done) and past simple (I did):
- ‘Was Tom at the party when you arrived?’ ‘No, he had already gone home.’
‘Was Tom there when you arrived?’ ‘Yes, but he went home soon afterwards.’ - Ann wasn’t at home when I phoned. She was in London.
Ann had just got home when I phoned. She had been in London.
Referensi
Murphy, Raymond. 1994. English Grammar In Use Second Edition. Syndicate Press: University of Cambridge.